Are you paying attention to your cervical fluid?
Cervical fluid is not something many women completely understand or pay attention to. It’s often thought to be some sort of vaginal infection due to a perception that things should always be dry ‘down there.’ Nevertheless, once you start observing this, you'll be able to recognize it as an important sign of fertility.
This is a misconception because there is a distinct pattern of cervical fluid during the cycle. Moreover, it has a distinct role in fertility, including:
-
Protecting the sperm in an otherwise acidic vagina
-
Nourishing the sperm
-
Allowing sperm to move freely
The Menstrual Cycle and Cervical Fluid
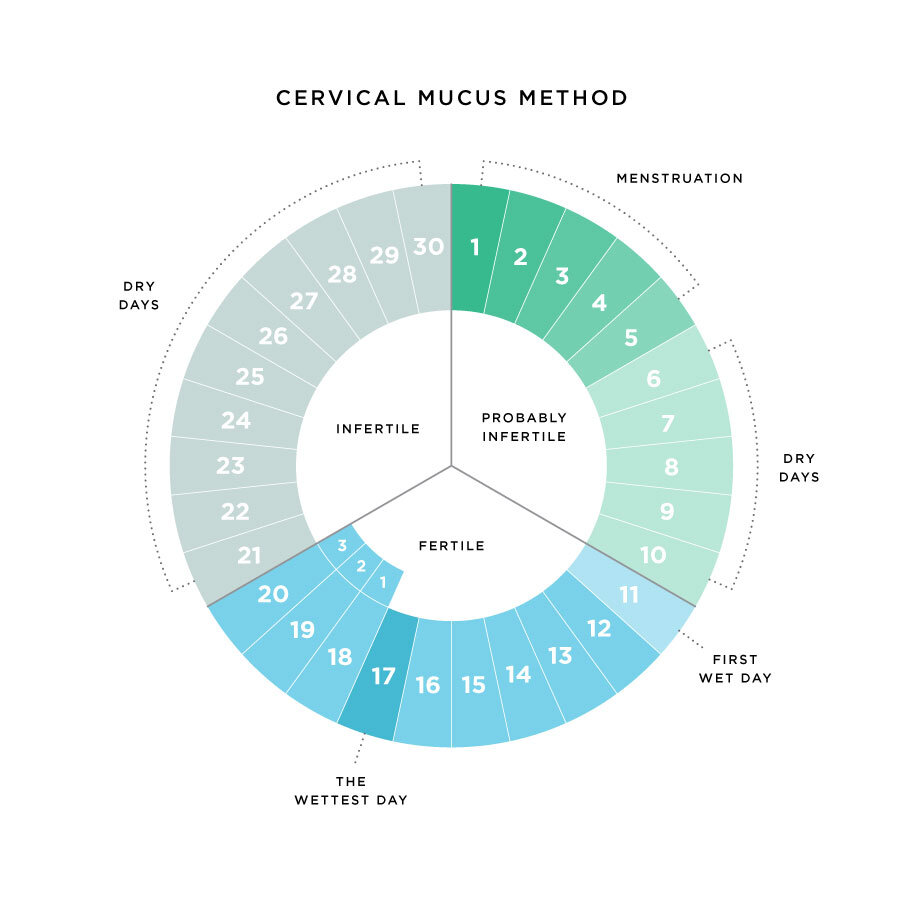
As demonstrated with the above picture, cervical fluid changes depending where you are in your menstrual cycle.
During your period, you likely won't be able to distinguish your cervical fluid from your blood flow.
After your period, there may be some days were you don't notice any cervical fluid. These would be considered dry days, and generally safe days if you are hoping to avoid a pregnancy.
As your body approaches ovulation, the texture and colour of cervical fluid begin to change. Fluid can be yellow, white, or cloudy and have a sticky or tacky texture.
A day before ovulation, this is when you will have the most cervical fluid. It looks clear and slippery like an egg white. If you are hoping to avoid pregnancy, this is considered an 'unsafe day' to have unprotected and sex with ejaculation. If you are hoping for a pregnancy, this is one of the best days to have sex.
As estrogen decreases after ovulation, cervical fluid production will be on the decline. These are considered safe days if you are hoping to avoid pregnancy.
Types of Cervical Fluid
Dry
Once your period is completed, you may not notice any cervical fluid because estrogen levels are still low. The feeling of dryness also occurs shortly after the wettest day due to the drop in estrogen levels and rise in progesterone.
Sticky
As estrogen levels begin to rise, you may begin to notice cervical fluid as it resembles a sticky consistency
Creamy
This fluid has more of a wet consistency and may resemble lotion. It may begin to stretch, but will end up breaking.
Egg white
This is considered the most fertile cervical fluid as it is clear, stretchy and has a slippery quality - that can provides a feeling of lubrication around ovulation. This type may also form a symmetrical circle on your underwear as it has a high concentration of water.
How to Observe Cervical Fluid
1. Start after you finish your period
2. Pay attention to your vaginal sensations - you don't need to do this all the time, but check in a couple of times during the day (like when you're heading to the restroom)
3. Check your cervical fluid. The best way to feel the consistency of your fluid is to rub it and stretch it between your thumb and index finger.
- Before urination, wipe the opening of your vagina with white toilet paper or tissue. Observe the colour and feel of the fluid.
- Look at your underwear for any discharge - note the colour and texture.
- Insert your clean fingers into your vagina, and note the colour and texture of cervical fluid on your fingers.
4. Record any findings on your BBT chart or app
Note: Arousal and semen can imitate fertile cervical fluid.
Conditions affecting Cervical Fluid
Certain activities or conditions can alter cervical fluid production and make this method less effective and difficult to use. These include:
-
Breastfeeding
-
Surgery on your cervix
-
Douching
-
Early menopause
-
Hormonal birth control
-
Sexually transmitted infections
-
Vaginitis
Final Thoughts
It might take a couple cycles to get acquainted with the patterns of your cervical fluid. Pairing this sign with your basal body temperature might give you more insight into your cycle and ultimately fertility.
If you love learning about your hormones and your period, be sure to sign up for my monthly newsletter called The Flow for great and informative content like this!
